Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
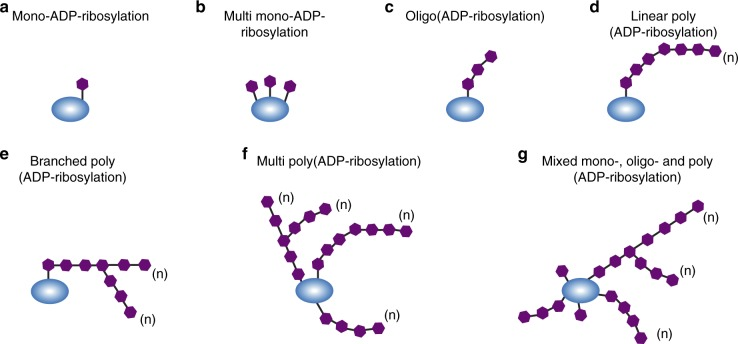
Struggle for research idea? Try protein ADP-ribosylation!ADP-ribosylation is a kind of post-translational modification, in which the enzyme ADP-ribosyltransferases (ARTs) use nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as a substrate to conjugate ADP-ribose to proteins, thereby regulating multiple cellular processes such as DNA repair, transcription, translation, cell signaling transduction and cell death. ADP-ribosylation on the target protein exists in various forms such as single, multiple, oligonucleotides, short linear, long linear, branching, etc., as shown in the figure below.
There are two main schemes for protein ADP-ribosylation: 1. Single ADP-ribosylation: ARTs link single ADP-ribose unit to protein 2. Multiple ADP-ribosylation: ARTs link multiple ADP-ribose units to protein to form ADP-ribose chains
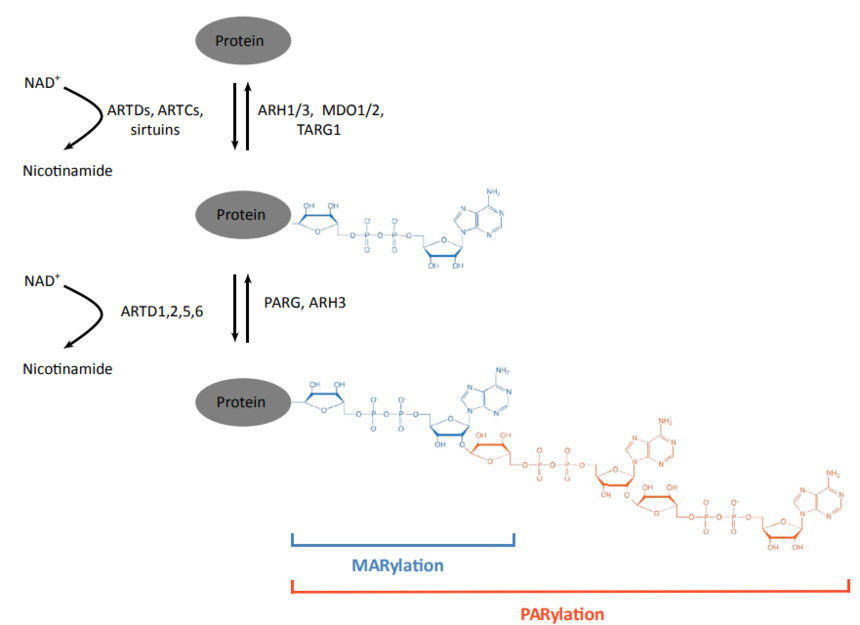
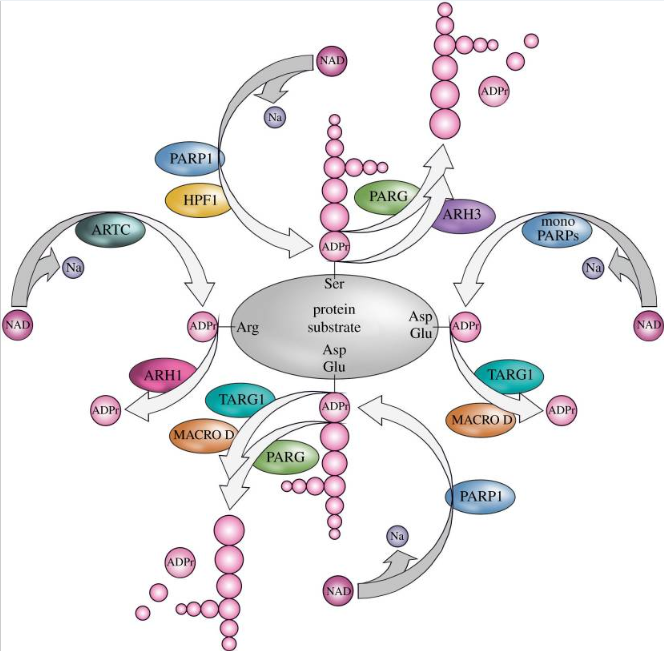
ARTs are the enzyme that catalyzes ADP-ribosylation. Mammals have two classes of ARTs, namely ADP-ribosyl transferases Cholera toxin-like (ARTCs) and ADP-ribosyl transferases Diphteria toxin-like (ARTDs). ARTDs consist of 18 intracellular Poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerases (PARPs). The following figure displayed the main mechanism of protein ADP-ribosylation.
Research revealed that dysregulation of enzymes involved in the regulation of ADP-ribosylation signaling is associated with many inherited and acquired human diseases. Therefore, in-depth study of ADP-ribosylation can provide new therapeutic routes for various diseases.
After sorting out relevant literature, we listed the research directions regarding ADP-ribosylation, which mainly include the following: 1. Exploring the regulatory mechanism of the structure of different structural domains of ADP-ribosylation on cellular processes 2. Analyzing active sites of ADP-ribosylation 3. Identifying ADP-ribosylation genes associated with human diseases 4. Dissecting the structure and function of proteins involved in ADP-ribosylation 5. Developing new inhibitors for cancer or inflammation-related diseases
Next, we would like to share literature related to ADP-ribosylation with a high IF.
This literature was published in the top journal of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Cell Discovery, with a high IF of 33.5.
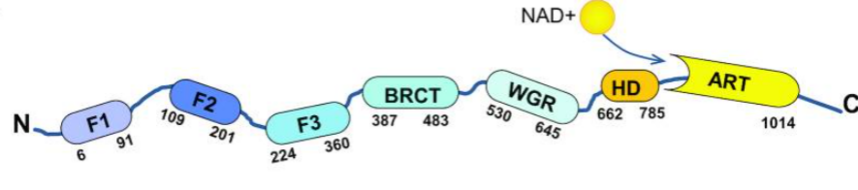
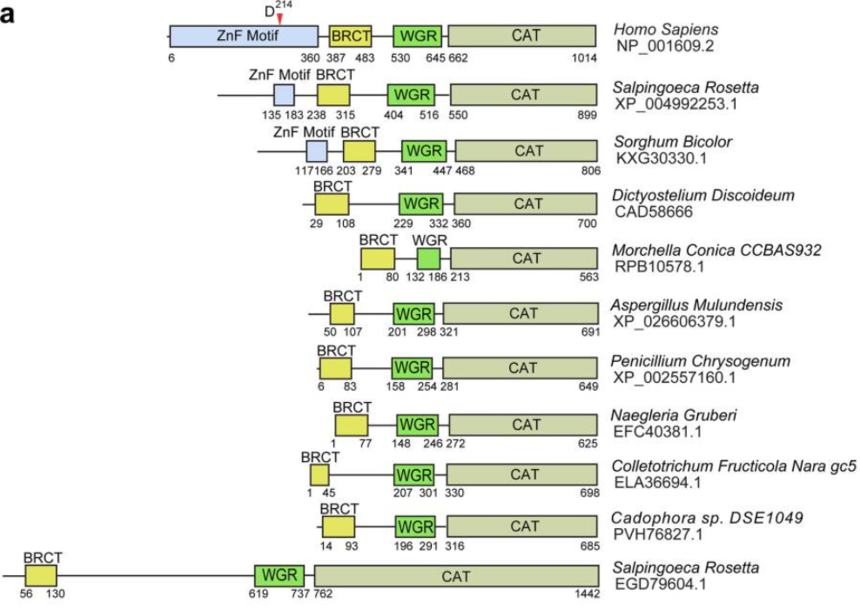
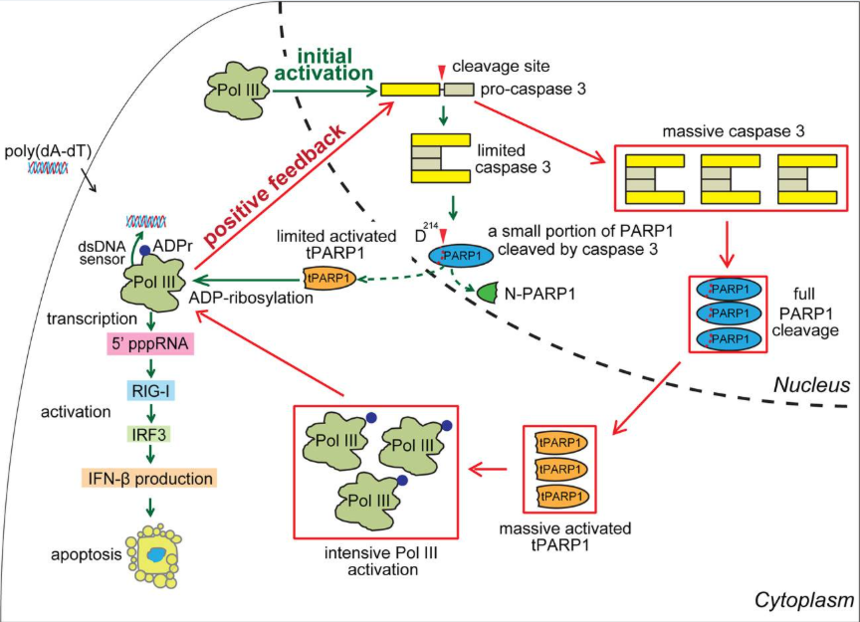
PARP1, a member of PARP family, can catalyze poly (ADP-ribosylation) on protein substrates, and participates in multiple cellular processes. The cleavage of PARP1 is a marker for apoptosis. During cell apoptosis, the first two zinc finger motifs (shown as F1 and F2 in the following figure) of PARP1 are cleaved mainly by caspase 3 to generate two fragments with 24 and 89 kD. The 89 kD truncated PARP1 (tPARP1) contains most domains and relocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Based on the above research background, the researchers conducted exploration pertaining to the biological function of tPARP1 in cell apoptosis.
First of all, the researchers, when probing into the structural domains of PARP1 in other organisms, found even if PARP1 orthologs in several lower organisms lack the two zinc finger motifs, tPARP1 still can catalyze ADP-ribosylation, which plays a critical role in some biological processes.
Then, the researchers identified the interplay between Pol III complex and tPARP1, and validated tPARP1 recognizes Pol III complex in cytoplasm during poly(dA-dT)-induced apoptosis and the ZnF3 or WGR domains are required for the ADP-ribosylation of tPARP1. Further, it has been documented that RNA Pol III subunits are substrates of tPARP1 and tPARP1-mediated ADP-ribosylation enhances the activity of cytosolic Pol III during apoptosis. Ultimately, they revealed that tPARP1-mediated ADP-ribosylation contributes to IFN response and promotes cell apoptosis.
In addition, we also sorted out other literature related to ADP-ribosylation available for retrieval and reading.
1£©Shigella evades pyroptosis by arginine ADP-riboxanation of caspase-11 2£©Deciphering ADP-ribosylation signalling 3£©Archaebacterial elongation factor is ADP-ribosylated by diphtheria toxin 4£©Catching mono- and poly-ADP-ribose readers with synthetic ADP-ribose baits 5£©ELTA: Enzymatic Labeling of Terminal ADP-Ribose 6£©Reversible ADP-ribosylation of RNA. 7£©ADP-Ribosylation as Post-Translational Modification of Proteins: Use of Inhibitors in Cancer Control 8£©Functional roles of ADP-ribosylation writers, readers and erasers 9£©An HPF1/PARP1-Based Chemical Biology Strategy for Exploring ADP-Ribosylation |