Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
Clarification on research hot spot | Neutrophils of immune cellsNeutrophil is a kind of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and makes up 50-70% of total leukocytes in human body, which is thus the most abundant immune cells in human body. Neutrophil is the first responder in congenital immunity, the number of which is applied to judge whether the body is suffering from bacterial or viral infection clinically.
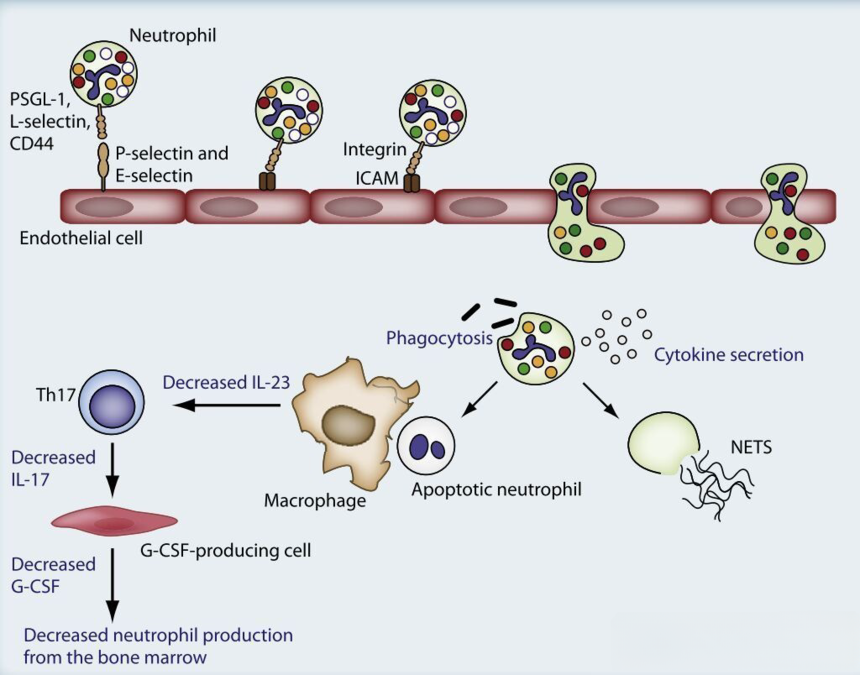
There are about 2.5×1012 mature neutrophils in bone marrow, which can enter into bloodstream according to the requirement of the body. A half of neutrophils in the blood vessel continue to circulate in the bloodstream, while the other half can adhere to the surface of vascular endothelial cells in the blood vessels and migrate across the endothelium into the tissue without returning to the blood. Generally, neutrophils entering the blood vessel maintain dynamic balance within a certain range, and their dynamic imbalance (with values increasing or decreasing) indicates the infection in the body.
Meanwhile, the infected organisms can incur neutrophil to phagocytize and kill bacterium, allowing neutrophils to participate in inflammatory responses.
How can neutrophils participate in the inflammatory response? What changes will occur in neutrophils after participating in the inflammatory response? There is an associated proper noun---neutrophil extracellular traps, meaning that activated neutrophils can capture and kill extracellular pathogens by releasing neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) composed of intracellular granular proteins and nuclear components such as DNA and histones into the extracellular space.
The formation of NETs is accompanied by death of neutrophils which is an inflammatory cell death pattern (termed NETosis) different from cell apoptosis and cell necrosis.
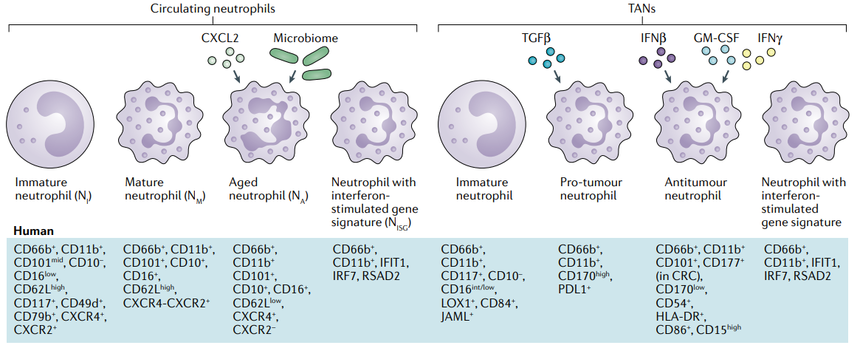
Moreover, neutrophils are important components of tumor microenvironment with the characteristics of heterogeneity and diversity. Apart from immature and mature neutrophils, there are tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) in tumors, which can not only participate in the inflammatory response of tumors by promoting angiogenesis, extracellular matrix remodeling, metastasis, and immune suppression, but also mediate anti-tumor responses via directly killing tumor cells and regulating the cell network of anti-tumor resistance.
Next, let’s dissect a relevant research paper published in Clinical and translational medicine.
In this study, authors successively explored the role of CsA in ASUC patients and neutrophils as well as corresponding mechanism. Then, based on the critical effect of SIRT6-HIF-1α signaling pathway on glucose metabolism regulation, this study investigated the impacts of SIRT6 and HIF-1α in CsA regulating neutrophils.
The ultimate results revealed that the limitation of CsA on neutrophil overactivation plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis and controlling overload pro-inflammatory responses, during which SIRT6-HIF-1α-dependent glycolytic signaling pathway plays an important role, and CsA promotes HIF-1α expression in neutrophils by suppressing SIRT6 expression and facilitates glycolysis and TCA cycle, thereby modulating the inflammatory response.
Also, we collect more other research paper related to neutrophils for your reference:
1) The Neutrophil's Role During Health and Disease 2) Cancer cells induce metastasis-supporting neutrophil extracellular DNA traps 3) Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Inflammation and Biomaterial Preconditioning for Tissue Engineering 4) Neutrophil plasticity in the tumor microenvironment 5) Neutrophil transendothelial migration: updates and new perspectives 6) Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Atherosclerosis and Atherothrombosis 7) Neutrophil migration in infection and wound repair: going forward in reverse 8) Neutrophil dysfunction in bronchiectasis: an emerging role for immunometabolism
|