Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
IF=11.3! What an ingenious idea for a glucose metabolic reprogramming report!Glucose metabolic reprogramming is a critical field in cancer research and a hallmark of cancer. To adapt hypoxia and nutrient deficiency, tumor cells must reprogram metabolic pathway to satisfy the requirements of energy, biosynthesis and redox, which is termed metabolic reprogramming.
There are 7 hallmarks of metabolic reprogramming, including increased glycolysis, increased pentose phosphate pathway, mitochondrial changes and TCA rewiring, increased lipid metabolism, increased glutaminolysis, changes in amino acid metabolism, and changes in other biosynthetic and bioenergetic pathways, which paly vital roles in the occurrence and development of tumors and virus pathogenesis.
Next, we take a paper with a high IF as an example to deeply understand the project design thinking regarding glucose metabolic reprogramming~
This paper was published on Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, with an IF of 11.3.
Research background: Ovarian cancer is a common gynecological malignancy in women, with high prevalence and incidence rates that affect the health of women. The standard therapies for ovarian cancer include surgical resection and chemotherapy, but patients still have a 5-year survival rate of < 50%. Thus, studying the molecular pathogenesis, and novel prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets is of high significance in prognosis and treatment of ovarian cancer.
Preliminary basis: 1. TRPM7 high expression is associated with pelvic lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of human ovarian cancer, and inhibition of TRPM7 can hinder the invasion and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells through attenuating Ca2+-PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 2. TRPM7 is highly expressed in various tumors, which can enhance the malignant behaviors of cancer cells. 3. Inhibition of TRPM7 can promote HIF-1α degradation in prostate cancer cells, and HIF-1α/AMPK signaling pathway is an important regulator participating in glucose metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation.
Therefore, the authors surmised that TRPM7 activation can regulate HIF-1α/AMPK signaling pathway, modulate glucose metabolism, and boost cancer cell proliferation.
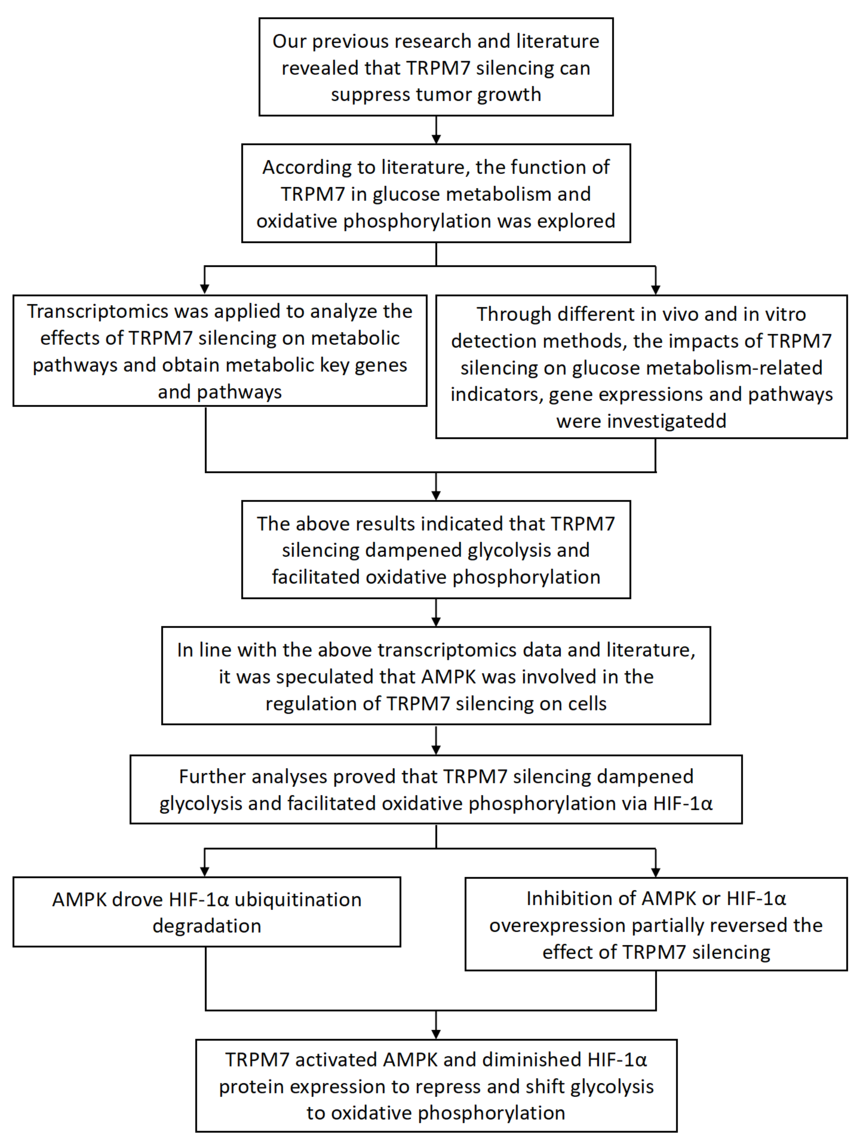
Research idea:
Specific mechanism: The following figure unveiled that the mechanism of glucose metabolic reprogramming of ovarian cancer cells, namely TRPM7 silencing suppressed glucose metabolism and promoted OXPHOS via regulating AMPK/HIF-1α signaling in ovarian cancer cells. Besides, TRPM7 silencing can enhance AMPK activation to boost the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of HIF-1α (i.e. promotion of HIF-1α degradation by ubiquitination), reduce the promoting effect of HIF-1α on glycolysis, shift glycolysis to OXPHOS, and block cell proliferation and tumor growth in ovarian cancer.
This finding unraveled the novel role of TRPM7 in ovarian cancer growth, and implied that TRPM7 may be the new therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. |