Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
IF=29.0! Yan Bi’s group in Nanjing University: seeking a new treatment strategy for cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetesFor memory loss in old people, a seasoned doctor can realize that beyond the superficial phenomenon, it is related to decline in cognitive function. Then, what are the design ideas for cognitive impairment?
Today, we will share a paper titled Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication of adipose tissue with brain and promote cognitive impairment associated with insulin resistance, published on Cell Metabolism with IF of 29.0, hoping to bring an inspiration.
1. Research background (1) Type 2 diabetes is associated with the increased risk of cognitive impairment, including mild cognitive impairment and dementia. (2) Glucose dysregulation is an established risk factor for cognitive impairment and controlling blood glucose has limited positive effects on cognitive function. (3) The abnormal function of adipose tissues plays a vital role in the occurrence of cognitive impairment. (4) The adipose tissues can secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs) as insoluble mediators, playing a role in inter-organ communication. (5) Whether EVs can mediate the communication between adipose tissues and central nervous system, especially in the worsening of brain pathology and cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes.
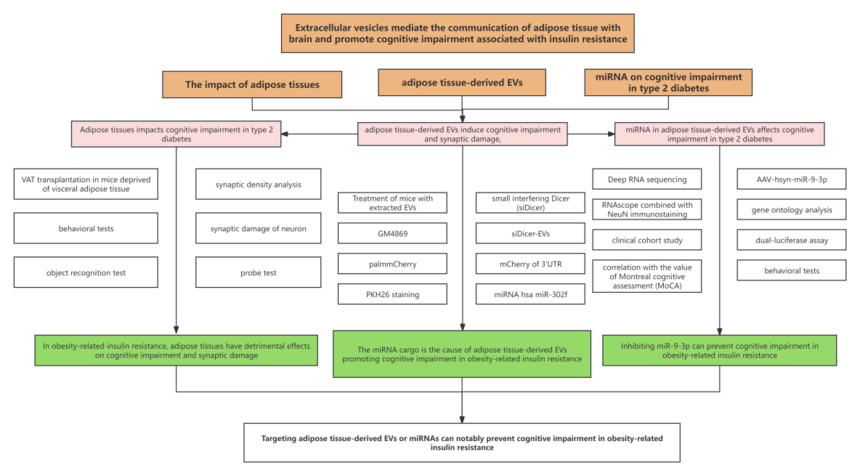
2. Technical route
3. Research results (1) Adipose tissues have detrimental effects on cognitive impairment in obesity-related insulin resistance. (2) The adipose tissue-derived EVs promote cognitive impairment and synaptic damage in obesity-related insulin resistance. (3) The adipose tissue-derived EVs can be transferred into the brain and enriched in neurons of hippocampus. (4) The miRNA cargo is the cause of adipose tissue-derived EVs promoting cognitive impairment in obesity-related insulin resistance. (5) The miRNAs in adipose tissue-derived EVs that can impact cognitive impairment in obesity-related insulin resistance have been identified. (6) MiR-9-3p targets BDNF to damage synapsis. (7) Inhibiting miR-9-3p can prevent cognitive impairment in obesity-related insulin resistance.
4. Research conclusion Type 2 diabetes mainly characterized by obesity-related insulin resistance is pertinent to an increased risk of cognitive impairment, during which adipose tissues play a pivotal role. Researchers confirmed that adipose tissue-derived EVs and their miRNAs mediate the inter-organ communication between adipose and brain. miRNAs are transferred into the brain in a membrane protein-dependent manner and enriched in neurons, especially in the hippocampus. The adipose tissue-derived EVs from high-fat diet-fed mice or patients with diabetes greatly induce synaptic loss and cognitive impairment. The depletion of miRNAs in EVs apparently mitigates their detrimental effects on cognitive function. Collectively, targeting adipose tissue-derived EVs or their miRNAs may serve as a promising strategy for drug intervention of cognitive impairment in diabetes. |