Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
Fang Lu’s group with a publication of 17.1 IF in the subdivision of Science: Here is the key mechanism of “gut-retina” axis regulating the onset of glaucomaEyes are pivotal sensory organs in the human body. Therefore, eye diseases not only bring visual damage or loss that leads to inconvenient life and work of patients, but also aggravate the burden of family and society. Then, what are the design ideas of research subjects related to eye diseases?
This article will introduce the design ideas based on a paper, Gut-licensed β7+CD4+T cells contribute to progressive retinal ganglion cell damage in glaucoma, published on Science Translational Medicine with IF of 17.1.
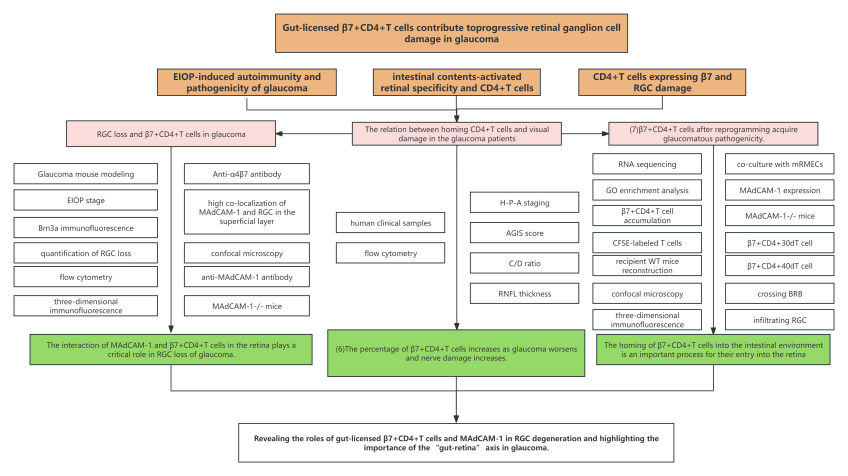
1. Research background (1) Elevated intraocular pressure (EIOP)-triggered autoimmune components participate in the secondary neurodegeneration of glaucoma. (2) T cells make great impacts upon the pathogenesis of progressive glaucomatous neural damage. (3) Extracts of intestinal contents can cross-activate CD4+ T cells and retina-specific T cell receptors, but the relevant mechanism remains unknown. (4) Intestinal barrier damage can result in damage of neurons in the inner layer of the mouse retina, where CD4+T cells expressing gut-homing molecule β7 play a crucial pathological role.
2. Technical route
3. Research results (1) The percentage of homing CD4+ T cells correlates with visual damage in patients with glaucoma. (2) RGC loss in progressive glaucoma is related to an increase in circulating β7+CD4+T cells in mice. (3) β7+CD4+T cells promote progressive RGC loss in glaucoma. (4) Ectopic retinal expression of MAdCAM-1 is required for progressive RGC damage. (5) β7+CD4+T cells after reprogramming obtain glaucomatous pathogenicity in mice. (6) β7+CD4+30dT cells induce MAdCAM-1 expression in retinal vessel to boost their entry into the retina. (7) β7+CD4+T cells homing to the intestinal environment is a vital process for their entry into the retina.
4. Conclusion Authors found that the percentage of circulating CD4+T cells expressing gut-homing integrin β7 increases, and β7+CD4+T cells infiltrate retina via inducing MAdCAM-1 expression in retinal endothelial cells. Further research indicated that EIOP-induced β7+CD4+T cells home to the gut during the acute phase of glaucoma. β7+CD4+T cells obtain the competence to induce retinal MAdCAM-1 expression and to cross the blood-retina barrier. These findings unveiled the roles of gut-licensed β7+CD4+T cells and MAdCAM-1, highlighting the importance of “gut-retina” axis in glaucoma. |