Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
IF of 11.7! Xiaochun Bai’s group in Southern Medical University revealed new mechanism of diabetic foot ulcer repair, publishing in Cell’s subsidiary journal!Diabetes is a metabolic disease characterized by persistent high glucose, possibly resulting from pancreatic β-cell damage-induced deficient production of insulin and/or reduced responses (or reduced insulin sensitivity) of body tissues to insulin secretion. What are the research design ideas about diabetes? Let’s explore based on the case~ Next, we share a paper entitled Bone transport induces the release of factors with multi-tissue regenerative potential for diabetic wound healing in rats and patients, with IF of 11.7 published on Cell Reports Medicine, hoping to inspire you from different aspects~
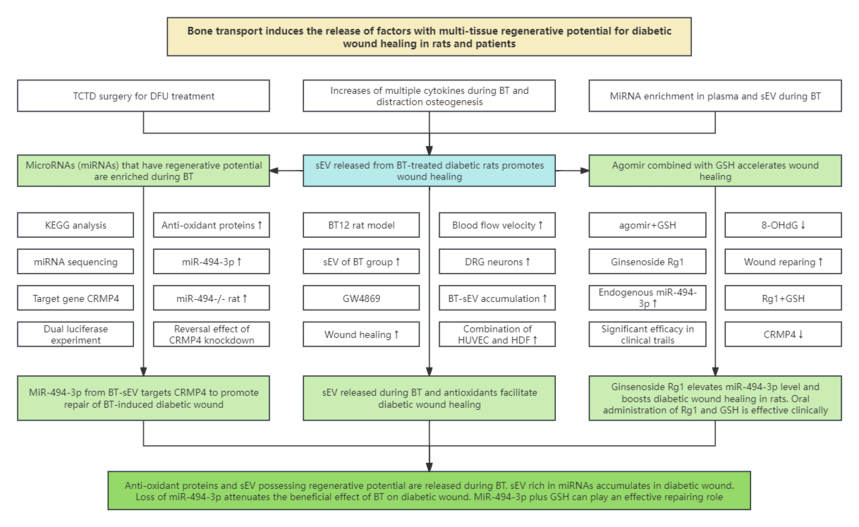
1. Research background 1.1 The Ilizarov bone transport (BT) surgery was originally developed to address some complex orthopedic diseases. 1.2 The improved Ilizarov tibial cortex transverse distraction (TCTD) is a new method based on the tension-stress effect for treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs); however, the risk of surgery and high cost restricted most DFU patients from using TCTD. 1.3 Multiple cytokines and hormones, such as vascular endothelial growth factor, bone morphogenetic protein, immune factors, and stromal cell-derived factors, are increased during BT and distraction osteogenesis. 1.4 Currently, there are no evidence showing the causal relation between these factors and BT-stimulated regeneration, and how regenerative ability is activated during BT remains unknown.
2. Technical routes
3. Research results 3.1 Release of sEV is critical for accelerating wound healing in diabetic patients and BT-treated rats 3.2 sEV released during BT has multi-tissue regenerative activity towards diabetic wound healing 3.3 Antioxidants and regeneration-promoting miRNA are enriched in plasma and sEV during BT 3.4 MiR-494-3p targets CRMP4 and promotes healing of BT-induced diabetic wound 3.5 Rg1 or agomir-494-3p and GSH in combination can facilitate wound healing in diabetic mice 3.6 Oral administration of Rg1 and GSH enhances wound healing in refractory DFU patients 4. Conclusions This study revealed that human and rats release anti-oxidant proteins and sEV with multi-tissue regeneration potential during BT. These vesicles accumulate in diabetic wound and are rich in miRNAs (such as miR-494-3p) possessing high regenerative abilities, which can improve blood circulation in the ischemic lower extremities and promote angiogenesis, fibroblast migration and nerve fiber regeneration. MiR-494-3p deficiency in rats can reduce the beneficial effects of BT on diabetic wound, while hydrogel containing miR-494-3p and GSH can repair wound effectively. More importantly, ginsenoside Rg1 can up-regulate miR-494-3p. A randomized controlled trial confirmed that oral administration of Rg1 and GSH accelerates wound healing in patients with refractory DFU. These findings identify functional factors with tissue regeneration potential and provide a prospective therapy for DFU. |