Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
Attention: the most powerful combination comes! The team in Anhui Medical University successfully published a paper with 12.2 IF in the field of the emerging “SUMOylation” in NSFC + the most popular “Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMU) is a newly found ubiquitin-like molecule, many kinds of which have been confirmed to be ubiquitin-like proteins in recent years. SUMOylation is a kind of critical protein post-translational modification. Then, what are the design ideas about SUMOylation?
Next, we will share a paper published on Journal of Hazardous Materials with an IF of 12.2, entitled ALKBH5 SUMOylation-mediated FBXW7 m6A modification regulates alveolar cells senescence during 1-nitropyrene-induced pulmonary fibrosis, hoping to inspire you from different aspects.
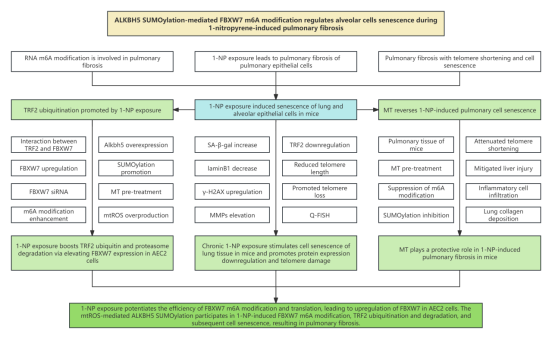
1. Research background 1.1 1-nitropyrene(NP) exposure leads to pulmonary fibrosis of pulmonary epithelial cells 1.2 Alveolar epithelial cells type II (AEC2) senescence is a main contributor to the occurrence of pulmonary fibrosis 1.3 Pulmonary interstitial fibrosis patients experience telomere shortening and cell senescence. However, whether chronic 1-NP exposure causes telomere damage and cell senescence during pulmonary fibrosis remains unknown. 1.4 RNA m6A modification is involved in the occurrence and development of pulmonary fibrosis, and the dynamic equilibrium of RNA m6A modification is of great significance for maintaining cell senescence 1.5 Whether RNA m6A modification is associated with 1-NP-induced cell senescence and pulmonary fibrosis still awaits discovery
2. Technical route
3. Research results 3.1 Chronic 1-NP exposure induces senescence of lung and alveolar epithelial cells in mice 3.2 Chronic 1-NP exposure induces telomere damage of lung and alveolar epithelial cells in mice 3.3 1-NP promotes TRF2 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation via FBXW7 in alveolar epithelial cells 3.4 1-NP enhances FBXW7 m6A modification in alveolar epithelial cells in a ALKBH5-YTHDF1-dependent manner 3.5 In MLE-12 cells, 1-NP facilitates ALKBH5 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation by SUMOylation 3.6 1-NP mediates ALKBH5 SUMOylation in MLE-12 cells via mtROS 3.7 MT pre-treatment reduces 1-NP-induced telomere damage and cell senescence in mouse liver 3.8 MT pre-treatment mitigates 1-NP-induced pulmonary fibrosis 4. Conclusion This study found that 1-NP can induce telomere damage and cell senescence in mouse lungs and two alveolar epithelial cell lines. 1-NP reduces TRF2 level and increases FBXW7 level. Mechanistically, 1-NP-induced TRF2 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation depends on E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of FBXW7. 1-NP upregulates FBXW7 m6A modification in an ALKBH5-YTHDF1-dependent manner. Further analysis results revealed that 1-NP promotes ALKBH5 SUMOylation and subsequent proteasomal degradation, and also induces mtROS overproduction. Mito-TEMPO, a mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant, mitigates 1-NP-caused mtROS overproduction, ALKBH5 SUMOylation, FBXW7 m6A modification, TRF2 degradation, cell senescence, and pulmonary fibrosis. Collectively, mtROS-induced ALKBH5 SUMOylation and subsequent FBXW7 m6A modification are necessary for TRF2 degradation and cell senescence in alveolar epithelial cells. This study provides target intervention methods for 1-NP-induced pulmonary fibrosis. |