Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
“Cell autophagy + Diabetes”: A Clever Approach Secures an IF of 14.6 in Zone 1 of the Chinese Academy of Sciences! The Team of Han Xiao/Chen Fang from Nanjing Medical University Proposed A New PerspecSimply put, cell autophagy means “cells eat themselves”, which is an important process in eukaryotes that is evolutionarily conserved for the recycle of intracellular materials. Then, what are design ideas of project about cell autophagy? Today, let’s discuss together.
Today, we will share a paper published on Autophagy in zone 1 of the Chinese academy of sciences with an IF of 14.6, hoping to bring different inspirations.
1. Research background 1.1 EGCG is the main active catechins in green tea, displaying wide function characteristic in the protection of pancreatic islets and β cells; 1.2 In BECN1F121A mice with over-active autophagy, due to excessive degradation of insulin granules, excessive induction of autophagy can reduce secretion and storage of insulin; 1.3 Previous findings suggested that the glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1)/FTO axis mediates excessive autophagy and induces β cell dysfunction; 1.4 Overexpression of RNA demethylase FTO promotes the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species and NFKB/NF-κB activation, thereby causing impaired mitochondrial oxidative function and decreased β cell insulin secretion.
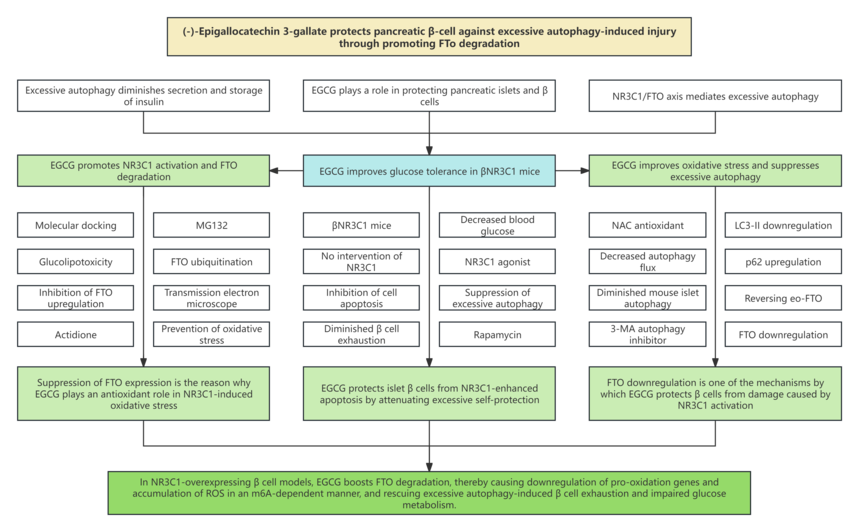
2. Technical routes
3. Research results 3.1 EGCG can improve the glucose tolerance and β cell function in β cell-specific NR3C1 overexpression mice 3.2 EGCG reverses NR3C1 activation-induced pancreatic β cell exhaustion 3.3 EGCG protects islet β cells from NR3C1-induced apoptosis by inhibiting excessive autophagy 3.4 EGCG boosts NR3C1 enhancement-activated FTO degradation of β cells 3.5 EGCG hinders NR3C1-indcued oxidative stress via dampening FTO expression 3.6 EGCG blocks FTO-induced excessive autophagy by improving oxidative stress 3.7 EGCG plays a protective role in NR3C1 activation-induced β cell damage, and its mechanism may be related to FTO downregulation
4. Conclusion This research explored the potential protective effects of EGCG on β-cell-specific NR3C1 overexpression mice in vivo and NR3C1-enhanced β cells in vitro, and found that EGCG protects pancreatic β cells from NR3C1 enhancement-induced exhaustion by inhibiting excessive autophagy. RNA demethylase FTO (FTO α-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenase) leads to reduced m6A modifications on the mRNA of three pro-oxidative genes (Tlr4, Rela, Src), resulting in oxidative stress. In contrast, EGCG promotes the degradation of FTO through the ubiquitin-proteasome system in NR3C1-enhanced β cells, thereby reducing oxidative stress and preventing excessive autophagy. In conclusion, this research indicated that EGCG protects pancreatic β cells from NR3C1 enhancement-induced excessive autophagy by inhibiting FTO-stimulated oxidative stress, which provides new insights into the mechanism of the anti-diabetes effects of EGCG. |