Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
IF of 9.2 in CAS Zone 1! New Advanced Ideas in the “MAPK + liver injury”! Xiao Ma’s team from Chengdu University of TCM Reveals Paeoniflorin Protects Against APAP-Induced Hepatocyte InjuryMAPK belongs to Ser/Thr kinase family, which plays a critical role in complex cellular programs such as proliferation, differentiation, development, transformation, inflammatory responses, and apoptosis via transmitting, amplifying, and integrating signals from various stimuli and triggering appropriate physiological responses. So, what are some research design ideas related to the MAPK signaling pathway? Let’s explore them together today.
Next, we’ll share a paper published on Cell Mol Biol Lett with an IF of 9.2, hoping to inspire you from different aspects.
Research Background
1. In recent years, drug-induced liver injury (DILI) has become one of the leading causes of acute liver failure worldwide, particularly acetaminophen (APAP)-induced acute liver injury.
2. The activation or inhibition of upstream signals in the MAPK/mTOR pathway, especially alterations in kinases such as ERK, JNK, and p38, have been proved to be vital in liver injury.
3. Paeoniflorin (PF), a monoterpene glycoside extracted from traditional Chinese medicinal herbs such as Paeonia suffruticosa Andr., Paeonia lactiflora Pall. or Paeonia veitchii Lynch, possesses notable hepatoprotective effects and has been applied for treating liver fibrosis, cholestasis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Technical routes
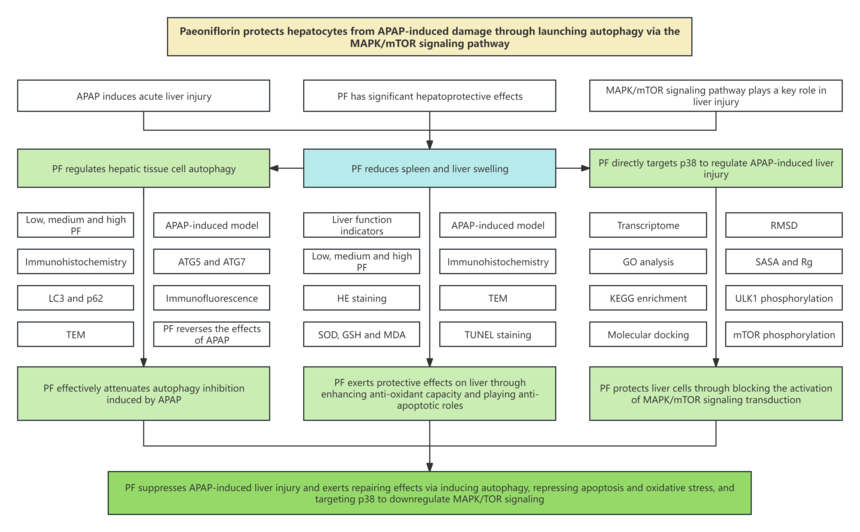
Research results 1. PF alleviates pathological changes of APAP-induced liver injury 2. PF dampens ROS to strengthen the antioxidative capacity of APAP-induced model mice 3. PF inhibits cell apoptosis of APAP-induced liver injury 4. PF activates autophagy to protect liver from APAP-induced injury 5. Transcriptomics reveals the mechanism of PF in APAP-induced liver injury 6. PF blocks the MAPK/mTOR signaling pathway by directly targeting p38
Research conclusions The study found that PF can decrease serum levels of ALP, γ-GT, AST, TBIL and ALT in APAP-induced mice, and apparently mitigate liver tissue inflammation and edema. Meanwhile, TUNEL staining results are consistent with the results of relevant apoptosis factors and transcriptomics, indicating that PF suppresses liver cell apoptosis by mediating MAPK signaling. In addition, PF impacts ROS, regulates oxidative stress, and repair damaged mitochondria. More importantly, transmission electron microscopy reveals the generation of autophagosome following PF treatment. Also, PF downregulates the mRNA level of mTOR and upregulates those of autophagic indicators including ATG5, ATG7 and BECN1. The protein levels of LC3, p62 ATG5 and ATG7 have been detected, confirming that the effects of PF are accompanied with autophagy. The data of MAPK molecular dynamics simulation and Western blot hint that p38 is a direct target of PF against APAP.
In conclusion, the study evidences that PF stimulates autophagy by downregulating MAPK/mTOR signaling via targeting p38, inhibits cell apoptosis and oxidative stress, and represses the critical process of APAP-induced liver injury, thereby exerting repairing effects.
|