Please click the button below to go to our email login page
|
IF=14.7. NC reveals TGFβ-SMAD signaling pathway and DNA methylation regulate the fate of embryonic stem cellsTGF-β is a secretary polypeptide cytokine, and acts as signal molecule between cells. Its mature form is composed of two connected TGF-β monomer and it forms a dimer through disulfide bonds. The main function of TGF-β is to regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, invasion and extracellular matrix formation. Then, what s the research subject design idea regarding TGFβ/SMAD signaling pathway?
Next, we’ll share a paper published on Nature Communications with IF of 14.7, hoping to inspire you from different aspects.
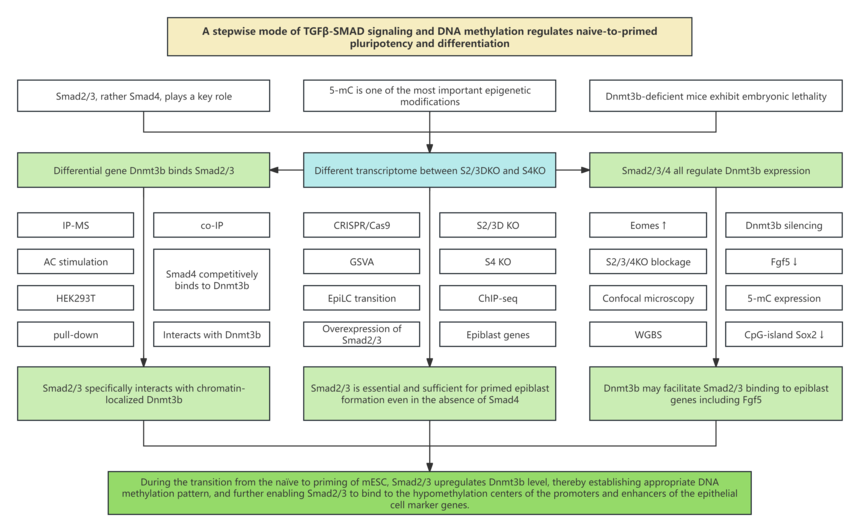
Research background 1. In pancreatic development process, Smad2/3 instead of Smad4 plays a key role. 2. DNA methylation at carbon 5 of cytosines (5-methylcytosine, 5-mC) is one of the most important epigenetic modifications. 3. During the transition from the pre- to the post-implantation epiblast of the embryo, the de novo DNA methyltransferases, DNA methyltransferase 3a (Dnmt3a) and DNA methyltransferase 3b (Dnmt3b), are greatly upregulated, and Dnmt3b-deficient mice exhibit embryonic lethality. 4. Smad2/3 loss in early-stage embryonic bodies (EBs) results in decreased RNA levels of Dnmt3b
Technical routes
Research results 1. Differential transcriptome between S2/3DKO and S4KO 2. Differential requirement for Smad2/3 and Smad4 during mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) differentiation 3. Formation of epiblast cells in the absence of Smad4 4. Genome-wide binding profile of Smad2/3 without Smad4 5. Dnmt3b interacts with Smad2/3 6. Upregulation of Dnmt3b by Smad2/3 is important for epiblast formation 7. Catalytically active Dnmt3 is required for epiblast induction 8. Dnmt3b mediates Smad2/3 binding to epiblast genes independently of Smad4
Conclusion This research introduces a stepwise mode, in which Smad2/3 regulates the lineage priming and differentiation of mESCs by collaboration with different effectors. During the naïve-to-primed transition, Smad2/3 upregulate Dnmt3b, which establishes the proper DNA methylation patterns and, in turn, enables Smad2/3 binding to the hypomethylated centers of promoters and enhancers of epiblast marker genes. Hence, in the absence of Smad2/3, Smad4 alone fails to initiate epiblast-specific gene transcription. When primed epiblast cells begin to differentiate, Dnmt3b becomes less actively engaged in global genome methylation, and Smad4 forms a complex with Smad2/3 to support mesendoderm induction. Accordingly, Smad-deficient mESCs can undergo initiation process, but encounters challenges in downstream differentiation. This research reveals the complex mechanism of TGFβ signaling and its role in cellular processes. |